20 Divided By 200
renascent
Sep 17, 2025 · 5 min read
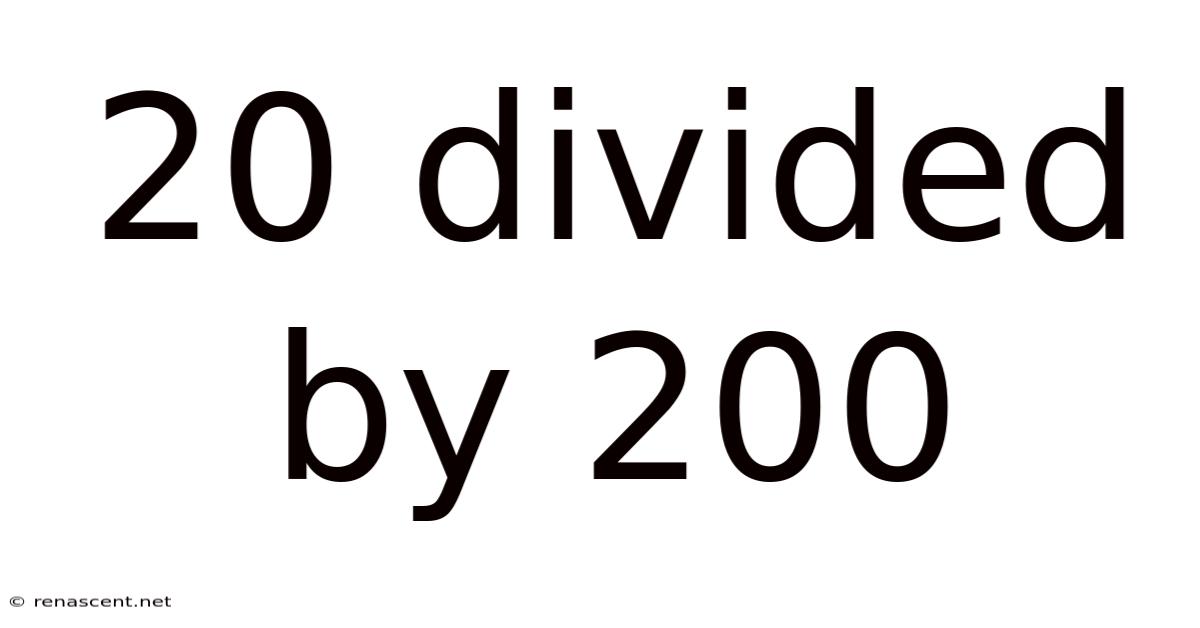
Table of Contents
20 Divided by 200: A Deep Dive into Division and Decimal Representation
This article explores the seemingly simple mathematical problem of 20 divided by 200, going beyond the immediate answer to delve into the underlying concepts of division, decimal representation, and their practical applications. Understanding this seemingly basic calculation unlocks a deeper appreciation for fundamental mathematical principles and their relevance in various fields. We'll cover the calculation itself, explore different methods of solving it, and examine the significance of the result in real-world scenarios.
Understanding Division: The Basics
Before tackling 20 divided by 200, let's refresh our understanding of division. Division is one of the four fundamental arithmetic operations, alongside addition, subtraction, and multiplication. It represents the process of splitting a quantity into equal parts. In the expression "a ÷ b" or "a/b," 'a' is the dividend (the number being divided), and 'b' is the divisor (the number by which we are dividing). The result is called the quotient.
Division can be interpreted in several ways:
- Sharing: Dividing a quantity into equal shares among a certain number of people. For instance, dividing 20 cookies among 5 friends means each friend receives 20 ÷ 5 = 4 cookies.
- Grouping: Determining how many groups of a certain size can be formed from a larger quantity. For example, if you have 20 apples and want to pack them into bags of 5 apples each, you can form 20 ÷ 5 = 4 bags.
- Scaling: Reducing a quantity proportionally. If a recipe calls for 20 units of an ingredient and you want to make a smaller version using only one-fifth of the original quantity, you would use 20 ÷ 5 = 4 units of the ingredient.
Calculating 20 Divided by 200
Now, let's tackle the specific problem: 20 ÷ 200. The simplest approach is to perform long division:
0.1
200|20.0
20.0
----
0
This shows that 20 divided by 200 equals 0.1. Alternatively, we can simplify the fraction:
20 ÷ 200 = 20/200
We can simplify this fraction by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common divisor, which is 20:
20/200 = (20 ÷ 20) / (200 ÷ 20) = 1/10
Since 1/10 is equivalent to 0.1, we arrive at the same result.
Decimal Representation and Significance
The result, 0.1, is a decimal number. Decimal numbers are a way of representing fractions where the denominator is a power of 10 (10, 100, 1000, etc.). The decimal point separates the whole number part from the fractional part. In 0.1, the '0' represents the whole number part (no whole units), and the '1' represents one-tenth (1/10).
The result of 0.1 in this context has significant implications. It highlights that the dividend (20) is smaller than the divisor (200). When the dividend is smaller than the divisor, the result is always a number between 0 and 1. This indicates a fractional portion, and the decimal representation provides a clear and concise way of expressing this fraction.
Alternative Methods and Conceptual Understanding
While long division and fraction simplification are the most straightforward methods, understanding alternative approaches can deepen our understanding of division.
-
Using Proportions: We can express the problem as a proportion: 20/200 = x/1. Solving for x involves cross-multiplication: 20 * 1 = 200 * x, which simplifies to 20 = 200x. Dividing both sides by 200 yields x = 0.1.
-
Mental Math: Recognizing that 20 is one-tenth of 200 allows for a quick mental calculation. Since 200 represents 10 times 20, dividing 20 by 200 effectively means finding one-tenth of 1, resulting in 0.1.
-
Calculator Use: For more complex division problems, a calculator provides a convenient and accurate solution. However, understanding the underlying concepts remains crucial, even when using technological aids.
Real-World Applications and Examples
The concept of dividing 20 by 200, while seemingly trivial, has practical applications in various fields:
-
Percentage Calculations: If 20 out of 200 students passed an exam, the pass rate is (20/200) * 100% = 10%. The calculation of 20/200 = 0.1 provides the decimal equivalent, which is then multiplied by 100 to express it as a percentage.
-
Scaling and Ratios: In architectural design, engineering, or recipe adjustments, scaling down dimensions or quantities requires division. If a blueprint shows a 200-unit measurement and you need to scale it down to 20 units, the ratio would be 20/200 = 0.1, indicating a reduction to one-tenth of the original size.
-
Financial Calculations: Calculating interest rates, returns on investment, or proportions of budgets involves division. For example, if an investment of 200 units yields a profit of 20 units, the return on investment is 20/200 = 0.1, or 10%.
-
Data Analysis: Analyzing datasets often involves calculating ratios and proportions, which necessitate division. For example, if a survey shows 20 respondents out of 200 prefer a particular product, the preference rate is 20/200 = 0.1 or 10%.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Why is the result a decimal and not a whole number?
A1: The result is a decimal because the dividend (20) is smaller than the divisor (200). When a smaller number is divided by a larger number, the result will always be less than 1, represented as a decimal.
Q2: Are there other ways to express the answer besides 0.1?
A2: Yes. The answer can be expressed as a fraction (1/10), a percentage (10%), or even as a ratio (1:10).
Q3: What if the order of the numbers was reversed (200 divided by 20)?
A3: Reversing the order would result in 200/20 = 10. This is because the dividend becomes larger than the divisor, resulting in a whole number quotient.
Q4: Can this type of calculation be applied to more complex scenarios?
A4: Absolutely. The fundamental principles of division remain the same, even when dealing with larger numbers, decimals, or more complex mathematical problems. This simple example provides a strong foundation for understanding more advanced concepts.
Conclusion: Beyond the Numbers
While the calculation of 20 divided by 200 might seem rudimentary, it serves as a springboard to understanding crucial mathematical concepts such as division, decimal representation, and their far-reaching applications. Mastering this seemingly basic operation lays a strong foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems in various disciplines. Remember, the key is not just to obtain the answer (0.1), but to grasp the underlying principles and their significance in real-world contexts. This understanding empowers you to approach numerical challenges with confidence and insight.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
98 4 Fahrenheit To Celsius
Sep 17, 2025
-
Smaller Than 3 8
Sep 17, 2025
-
7 Years In Days
Sep 17, 2025
-
55 Gallon To Litres
Sep 17, 2025
-
51 60 As A Percentage
Sep 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 20 Divided By 200 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.