3 X 7 5
renascent
Sep 15, 2025 · 6 min read
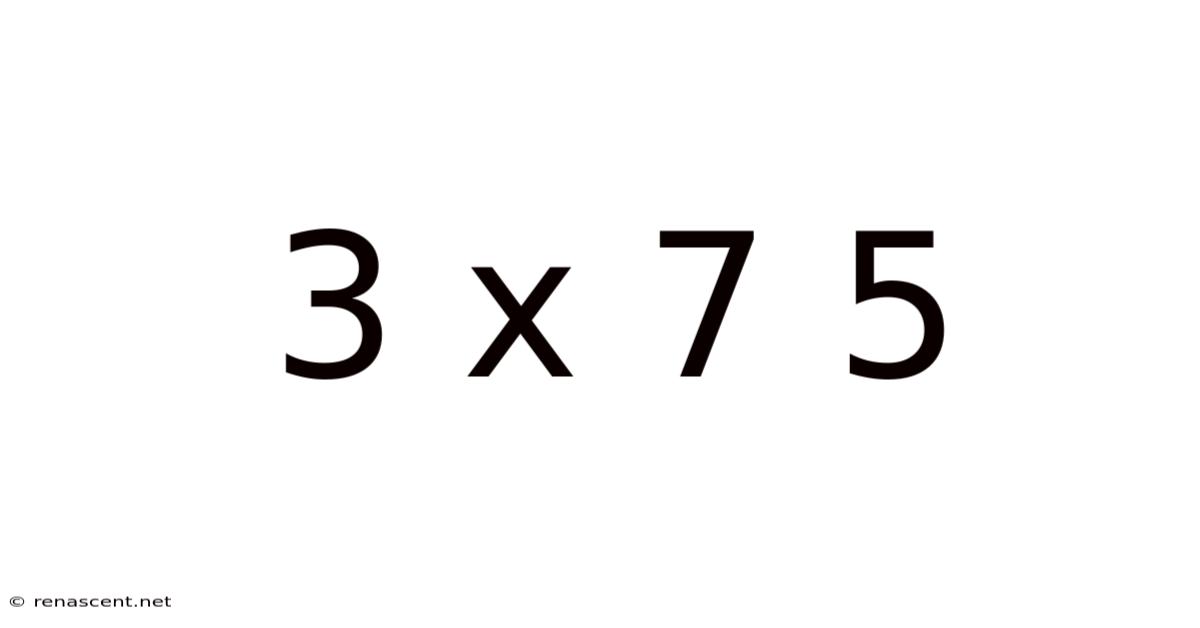
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: A Deep Dive into 3 x 7 = 5 (and Why It's Not True)
This article explores the seemingly paradoxical equation "3 x 7 = 5". While mathematically incorrect in standard arithmetic, this expression can represent various concepts depending on context. We'll delve into the possibilities, examining different mathematical systems, potential symbolic interpretations, and the importance of understanding the foundational principles of arithmetic. This journey will not only clarify why 3 x 7 doesn't equal 5 in conventional math but will also highlight the richness and flexibility of mathematical thinking.
Introduction: The Allure of the Incorrect
The statement "3 x 7 = 5" immediately grabs attention because it contradicts a fundamental truth learned in elementary school. This inherent contradiction sparks curiosity; it prompts us to question assumptions and explore alternative interpretations. The seemingly simple equation opens a door to a deeper understanding of mathematical systems, the importance of context, and the potential for symbolic representation beyond the familiar. We'll explore different scenarios where this equation, while false in standard arithmetic, might hold meaning.
Understanding Basic Multiplication: A Refresher
Before venturing into more complex interpretations, let's solidify our understanding of basic multiplication. Multiplication is essentially repeated addition. 3 x 7 means adding the number 3 seven times: 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 21. Therefore, within the standard decimal number system we use daily, the equation 3 x 7 = 21 is unequivocally true. Any deviation from this result requires a departure from standard arithmetic rules.
Exploring Alternative Mathematical Systems: Modular Arithmetic
One potential explanation for the equation "3 x 7 = 5" lies in modular arithmetic. Modular arithmetic is a system where numbers "wrap around" after reaching a certain value, called the modulus. For example, in modulo 8 arithmetic (denoted as mod 8), numbers cycle through 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, then back to 0.
Let's see how this applies:
- Standard multiplication: 3 x 7 = 21
- Modulo 8 arithmetic: 21 divided by 8 leaves a remainder of 5. Therefore, in mod 8, 3 x 7 ≡ 5 (mod 8).
This congruence means that in the context of modulo 8 arithmetic, the statement "3 x 7 = 5" is true. This highlights that mathematical operations can yield different results depending on the system used. The crucial aspect here is understanding the context—the underlying mathematical framework within which the calculation is performed. Without specifying the modulus, the equation remains mathematically false in standard arithmetic.
Beyond Numbers: Symbolic Representation and Abstract Thinking
The equation "3 x 7 = 5" could also represent a symbolic or abstract concept, unrelated to direct numerical calculations. Consider these possibilities:
-
Metaphorical representation: The equation might symbolize a transformation or a process where three units of something combine with seven units of something else to yield five units of a new entity. This requires defining what "3," "7," and "5" represent in this particular context. For example, three ingredients combined with seven processes may result in five end products.
-
Coded message: It could be part of a code or cipher where the numbers represent letters or symbols. Cracking the code would require additional information or a key to decipher its meaning.
-
Artistic expression: In art or literature, the equation could be used to evoke a feeling, create a sense of mystery, or challenge the viewer's/reader's perception of mathematical truth. The incongruity itself becomes the artistic statement.
The Importance of Context and Precision in Mathematics
The "3 x 7 = 5" example emphasizes the crucial role of context and precision in mathematical statements. Mathematics isn't simply a collection of formulas; it's a system of logic and reasoning built on clearly defined axioms and rules. A statement's validity hinges entirely on the system in which it's interpreted. To avoid ambiguity and misinterpretations, clarity is paramount. Always specify the mathematical system being used (e.g., modulo 8 arithmetic) to prevent confusion.
Addressing Common Misconceptions: Why It's Not "True" in Standard Arithmetic
Let's explicitly address why the equation "3 x 7 = 5" is inherently false in standard arithmetic, the mathematical system used for everyday calculations:
-
Fundamental axioms: Standard arithmetic is built upon axioms that define basic operations like addition and multiplication. These axioms guarantee that 3 x 7 will always equal 21 in a standard number system.
-
Consistency and predictability: The reliability of mathematics stems from its consistency and predictability. If 3 x 7 could equal both 21 and 5 depending on the whim of the interpreter, mathematics would be rendered useless for practical applications.
-
Logical fallacy: Accepting "3 x 7 = 5" in standard arithmetic creates a logical contradiction that invalidates numerous other mathematical theorems and processes dependent on the fundamental rules of arithmetic.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can any equation be "true" in a specific mathematical context?
A: While many equations can be made "true" within a specific context (like modular arithmetic), it’s crucial to remember this changes the fundamental meaning and application of the equation. It's not about making any equation true but rather about understanding the system in which it holds validity.
Q: Are there other examples of context-dependent mathematical equations?
A: Yes, many mathematical concepts depend on the context. For instance, the definition of "infinity" varies depending on the branch of mathematics. Different geometries also employ different sets of rules and axioms.
Q: How can I avoid making this kind of mistake?
A: Always clarify the mathematical system or context in which you're working. Pay close attention to the definitions and axioms of the specific system before attempting to solve an equation. Double-check your work, and ensure all operations adhere to the established rules.
Conclusion: The Power of Critical Thinking and Mathematical Exploration
While the equation "3 x 7 = 5" is demonstrably false within the framework of standard arithmetic, its exploration has allowed us to examine different mathematical systems, ponder symbolic representations, and emphasize the importance of context. The initial seeming contradiction has served as a springboard to delve into richer mathematical concepts, demonstrating that mathematical truth is not absolute but dependent on the system within which it's considered.
The core takeaway is the power of critical thinking. Questioning established norms, exploring alternative perspectives, and understanding the underlying principles are essential for genuine mathematical understanding. The seemingly simple equation "3 x 7 = 5" highlights the multifaceted nature of mathematics, revealing its flexibility, its beauty, and the ever-present need for clarity and precision. It encourages a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of numerical systems and the importance of context in interpreting mathematical statements. The equation, while incorrect in its most basic sense, becomes a powerful tool for learning and understanding the broader world of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3 X 7 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.