420 Divided By 10
renascent
Sep 18, 2025 · 6 min read
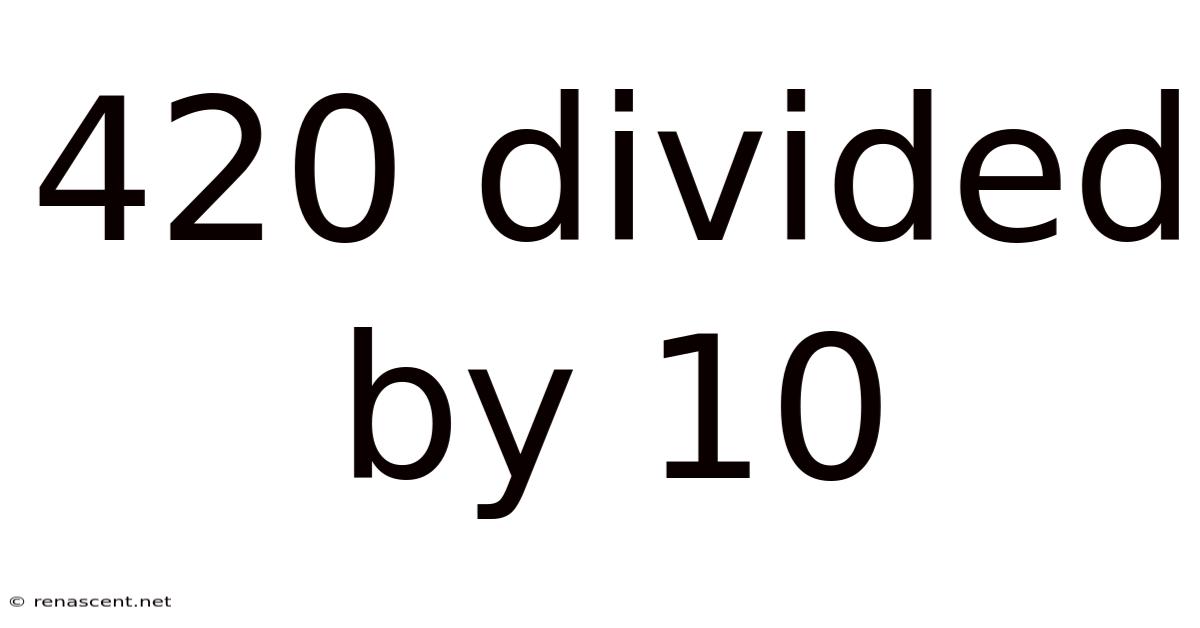
Table of Contents
420 Divided by 10: A Deep Dive into Division and its Applications
This article explores the seemingly simple calculation of 420 divided by 10, delving far beyond the immediate answer to illuminate the underlying principles of division, its practical applications, and its connection to broader mathematical concepts. We'll examine various methods for solving this problem, discuss its relevance in everyday life, and explore the significance of division within the broader context of arithmetic and beyond. Understanding this seemingly basic operation opens doors to a deeper appreciation of mathematical reasoning and its practical utility.
Introduction: Understanding Division
Division, at its core, is the inverse operation of multiplication. While multiplication involves combining equal groups, division involves separating a quantity into equal parts. The equation 420 ÷ 10 asks: "How many times does 10 fit into 420?" The answer, as we'll see in multiple ways, is 42. This simple problem forms the basis for understanding more complex division problems involving larger numbers, decimals, and even algebraic expressions.
Methods for Solving 420 ÷ 10
Several methods can be employed to solve 420 ÷ 10, each offering a different perspective on the underlying mathematical principles.
1. Long Division:
This traditional method involves a step-by-step process:
- Step 1: Set up the long division problem: 10 | 420
- Step 2: Divide the first digit (4) by 10. Since 10 doesn't go into 4, we move to the next digit.
- Step 3: Divide 42 by 10. 10 goes into 42 four times (4 x 10 = 40). Write the 4 above the 2 in 420.
- Step 4: Subtract 40 from 42, leaving a remainder of 2.
- Step 5: Bring down the 0 from 420, creating the number 20.
- Step 6: Divide 20 by 10. 10 goes into 20 two times (2 x 10 = 20). Write the 2 above the 0 in 420.
- Step 7: Subtract 20 from 20, leaving a remainder of 0.
Therefore, 420 ÷ 10 = 42.
2. Using Multiplication:
Division and multiplication are inversely related. To solve 420 ÷ 10, we can ask: "What number multiplied by 10 equals 420?" The answer, through mental calculation or a multiplication table, is 42.
3. Cancelling Zeros:
This method leverages the properties of place value. Since we're dividing by 10, which is a power of 10, we can simply remove one zero from 420. This leaves us with 42. This method works because dividing by 10 moves each digit one place to the right in the place value system.
4. Decimal Representation:
While not strictly necessary for this particular problem, understanding how division interacts with decimal numbers is crucial. If the dividend (420) wasn't perfectly divisible by the divisor (10), we would have a remainder, which we would represent as a decimal.
Practical Applications of Division
The operation 420 ÷ 10, while seemingly simple, has numerous real-world applications:
- Sharing Equally: Imagine you have 420 candies to distribute equally among 10 friends. Dividing 420 by 10 tells you each friend receives 42 candies.
- Calculating Averages: If you scored 420 points across 10 games, dividing 420 by 10 gives you your average score per game (42 points).
- Scaling Down: If you have a recipe that yields 420 cookies and you need to reduce it to 1/10th of the size, you would divide each ingredient quantity by 10.
- Unit Conversion: Many unit conversions involve division. For instance, converting 420 centimeters to meters requires dividing by 100 (since there are 100 centimeters in a meter). While not directly 420/10, it demonstrates the relevance of division in similar calculations.
- Financial Calculations: Dividing total expenses by the number of months helps determine monthly average spending. Similarly, dividing total profit by the number of units sold calculates the profit per unit.
- Rate and Ratio Problems: Numerous real-world situations involve rates and ratios. For example, if a machine produces 420 items in 10 hours, the production rate is 42 items per hour (420 ÷ 10).
Expanding the Concept: Division with Larger Numbers and Decimals
While 420 ÷ 10 is straightforward, the principles extend to more complex divisions. Consider:
- Dividing larger numbers: The same long division method, or other techniques like chunking (repeated subtraction), can be applied to larger numbers like 4200 ÷ 10 (420), 42000 ÷ 10 (4200), and so on. The pattern becomes apparent – each additional zero in the dividend results in an additional zero in the quotient.
- Dividing by decimals: Dividing by decimals involves adjusting the decimal point in both the dividend and the divisor to make the divisor a whole number before applying long division. For example, 420 ÷ 0.1 would be equivalent to 4200 ÷ 1 (4200).
The Significance of Division in Mathematics
Division plays a fundamental role in numerous mathematical concepts:
- Fractions: A fraction represents a division problem. For example, 420/10 is equivalent to the fraction 42/1, which simplifies to 42.
- Algebra: Algebraic expressions often involve division. Solving equations frequently requires dividing both sides of the equation by a common factor.
- Calculus: Derivatives and integrals in calculus involve concepts related to division and rates of change.
- Number Theory: Concepts like divisibility rules, prime numbers, and factors are all intrinsically linked to division.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What happens if I try to divide 420 by 0?
A1: Division by zero is undefined in mathematics. It's a fundamental rule. There is no number that, when multiplied by zero, equals 420.
Q2: Are there different types of division?
A2: While the basic concept remains the same, there are different types of division depending on the context, such as: * Exact division: When the division results in a whole number with no remainder (like 420 ÷ 10). * Division with a remainder: When the division results in a whole number with a remainder (like 425 ÷ 10 = 42 with a remainder of 5). * Decimal division: When the result is a decimal number (like 425 ÷ 10 = 42.5).
Q3: How can I improve my division skills?
A3: Practice is key. Start with simple problems like 420 ÷ 10 and gradually increase the complexity. Use different methods to solve problems and understand the underlying principles. Utilize online resources, worksheets, and educational apps to reinforce your learning.
Conclusion: Beyond the Answer
While the answer to 420 divided by 10 is simply 42, the journey to reach that answer reveals a wealth of mathematical principles and real-world applications. This seemingly simple calculation provides a solid foundation for understanding more advanced mathematical concepts, highlighting the interconnectedness of arithmetic operations and their profound impact on problem-solving across various disciplines. By mastering the principles of division, you unlock a powerful tool for understanding and interpreting the world around you. So, the next time you encounter a division problem, remember that it's not just about finding the answer; it's about appreciating the intricate mathematics behind it.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Word With Three Vowels
Sep 18, 2025
-
164 Pounds To Kilograms
Sep 18, 2025
-
11 F To C
Sep 18, 2025
-
The Looking Glass Self
Sep 18, 2025
-
83 F To C
Sep 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 420 Divided By 10 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.