53 F To C
renascent
Sep 15, 2025 · 5 min read
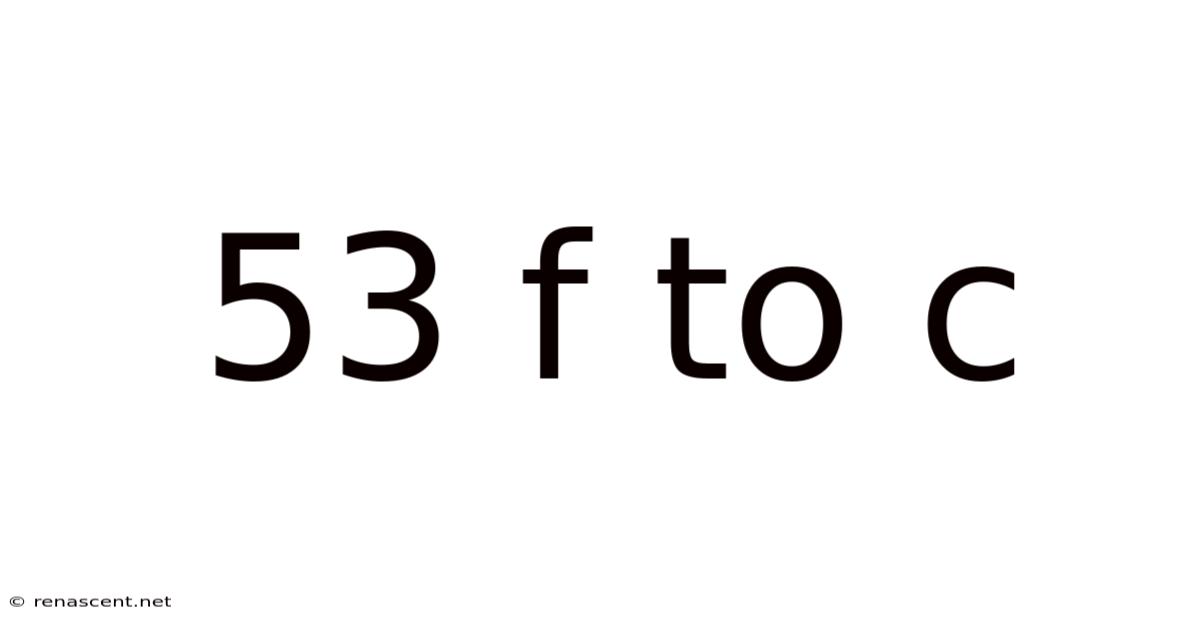
Table of Contents
53°F to °C: Understanding Temperature Conversions and Their Applications
Converting between Fahrenheit (°F) and Celsius (°C), the two most common temperature scales, is a fundamental skill in various fields, from everyday life to scientific research. This article will delve into the precise conversion of 53°F to °C, explain the underlying principles, and explore the practical applications of temperature conversions across diverse disciplines. We'll also address frequently asked questions and provide further insights to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Fahrenheit and Celsius Scales
Before jumping into the conversion of 53°F to °C, it's crucial to understand the historical context and differences between these two scales.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): Developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, this scale originally set 0°F as the freezing point of a brine solution (water, ice, and ammonium chloride) and 96°F as the average human body temperature. Later adjustments set the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F at standard atmospheric pressure.
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius was proposed by Anders Celsius in the 18th century. This scale sets 0°C as the freezing point of water and 100°C as its boiling point at standard atmospheric pressure. This linear relationship makes Celsius simpler for many scientific calculations.
The fundamental difference lies in the size of their degree increments and their zero points. Celsius has larger degree increments and a more intuitive zero point, making it the preferred scale in most scientific and international contexts.
Converting 53°F to °C: The Formula and Calculation
The conversion from Fahrenheit to Celsius involves a straightforward formula:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Let's apply this formula to convert 53°F to °C:
°C = (53 - 32) × 5/9 = 21 × 5/9 = 105/9 ≈ 11.67°C
Therefore, 53°F is approximately equal to 11.67°C.
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversions
The ability to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius is essential in numerous fields:
-
Meteorology: Weather reports often provide temperatures in both scales, requiring accurate conversions for international communication and data analysis. Understanding temperature ranges helps predict weather patterns and their impact on various activities.
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes from different regions may use either Fahrenheit or Celsius. Accurate conversion ensures consistent results in cooking and baking. Precise temperature control is crucial for many culinary techniques.
-
Medicine and Healthcare: Body temperature is frequently measured in both scales. Accurate conversions are necessary for comparing measurements, diagnosing illnesses, and administering medications. Maintaining optimal body temperature is crucial for human health.
-
Engineering and Manufacturing: Many industrial processes require precise temperature control. Converting between scales ensures accurate calibration of equipment and prevents errors in manufacturing processes. Temperature variations can affect the strength and properties of materials.
-
Scientific Research: Scientific experiments and data analysis often necessitate working with temperature values in Celsius, even if initial measurements are in Fahrenheit. Consistent units are crucial for reproducibility and data interpretation.
-
Environmental Science: Monitoring and analyzing temperature data, like global warming trends, requires seamless conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius to maintain data consistency across various sources. Understanding temperature changes is fundamental to environmental studies.
-
Everyday Life: Knowing how to convert temperatures helps in understanding weather forecasts, adjusting home thermostats, and even choosing appropriate clothing. This improves comfort and efficiency in daily tasks.
Beyond the Conversion: Understanding Temperature and Its Effects
While converting 53°F to °C is a simple calculation, understanding the implications of temperature is more profound. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles within a substance. Higher temperatures indicate faster-moving particles, resulting in various observable effects:
-
Phase Transitions: Temperature changes can cause substances to transition between solid, liquid, and gaseous states (melting, freezing, boiling, condensation, sublimation). Understanding these transitions is crucial in various industrial processes and scientific research.
-
Chemical Reactions: Temperature significantly impacts the rate and even the possibility of chemical reactions. Many reactions only occur within specific temperature ranges.
-
Biological Processes: Temperature plays a crucial role in biological processes. Enzymes, the catalysts of life, have optimal temperature ranges for their activity. Extreme temperatures can denature enzymes and disrupt cellular functions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why are there two different temperature scales?
A: Historically, different scales emerged independently based on different reference points and practical needs. Fahrenheit was initially based on readily available materials, while Celsius adopted a more rational system based on water's freezing and boiling points.
Q: Which temperature scale is more commonly used worldwide?
A: Celsius is the more widely used scale internationally, particularly in scientific and meteorological contexts. Fahrenheit is primarily used in the United States.
Q: Are there other temperature scales besides Fahrenheit and Celsius?
A: Yes, other scales exist, including Kelvin (K), which is the absolute temperature scale used in scientific research. Kelvin starts at absolute zero, where molecular motion theoretically ceases.
Q: How can I quickly estimate the conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius without a calculator?
A: A rough estimation can be obtained using the following approximations:
-
To convert Celsius to Fahrenheit, double the Celsius temperature and add 30. This is an approximation and may not be accurate for all values.
-
To convert Fahrenheit to Celsius, subtract 30 from the Fahrenheit temperature and then divide by 2. This too is an approximation, and its accuracy varies depending on the value.
These approximations are helpful for quick estimations but should not replace precise calculations for critical applications.
Conclusion
Converting 53°F to 11.67°C is a straightforward calculation, but the underlying principles and practical applications are far-reaching. Understanding temperature scales and their interconversion is crucial across various scientific, engineering, culinary, and everyday applications. This article has provided a comprehensive guide to the conversion, explored its relevance in diverse fields, and addressed frequently asked questions to deepen your understanding of this fundamental concept. The ability to accurately convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius enhances your problem-solving skills and broadens your scientific literacy. Remember that while quick estimations can be helpful, precise conversions are necessary for accurate results in critical contexts.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 53 F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.