54 Divided By 3
renascent
Sep 18, 2025 · 5 min read
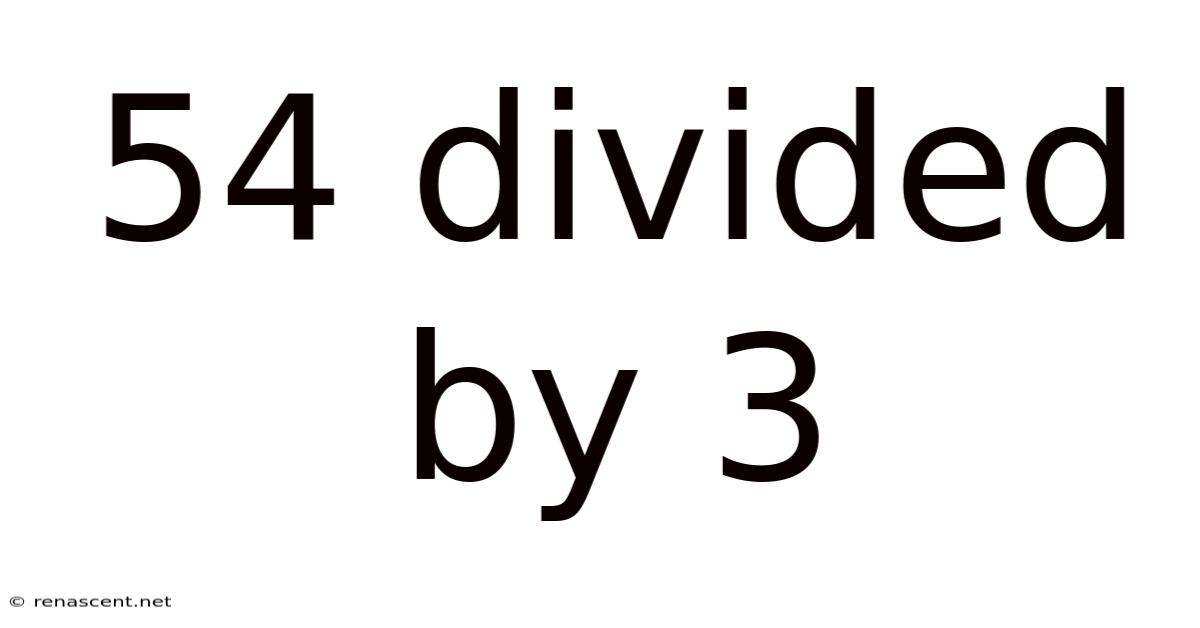
Table of Contents
Unpacking 54 Divided by 3: A Deep Dive into Division
This article will explore the seemingly simple calculation of 54 divided by 3, delving far beyond the immediate answer. We'll uncover the underlying mathematical principles, explore different methods for solving the problem, examine its real-world applications, and even touch upon the broader concepts of division within the context of arithmetic. Understanding this seemingly basic equation unlocks a deeper appreciation for the fundamentals of mathematics. By the end, you'll not only know the answer but also possess a comprehensive understanding of the process and its implications.
The Answer and its Immediate Significance
The answer to 54 divided by 3 is 18. This is a straightforward calculation, easily solved with a calculator or through basic long division. However, the significance of this simple calculation extends far beyond the immediate result. It forms the bedrock of more complex mathematical operations and is fundamental to numerous real-world applications.
Understanding Division: More Than Just Sharing
Division, at its core, represents the process of splitting a quantity into equal parts. In the case of 54 ÷ 3, we are essentially dividing the number 54 into three equal groups. This concept is crucial because it underlies various aspects of our daily lives, from sharing resources fairly to calculating unit prices and proportions.
Think of it this way: Imagine you have 54 cookies to distribute equally among 3 friends. Division helps you determine how many cookies each friend will receive. Each friend gets 18 cookies (54 ÷ 3 = 18). This simple example highlights the practical application of division in everyday life.
Methods for Solving 54 ÷ 3
Several methods can be employed to solve this division problem:
-
Long Division: This is a classic method taught in schools. It involves systematically dividing the dividend (54) by the divisor (3) to obtain the quotient (18).
18 3|54 3 -- 24 24 -- 0 -
Repeated Subtraction: This method involves repeatedly subtracting the divisor (3) from the dividend (54) until the remainder is zero. The number of times you subtract the divisor represents the quotient. This method, while potentially longer for larger numbers, visually reinforces the concept of division as repeated subtraction.
-
Multiplication: Since division is the inverse operation of multiplication, we can find the answer by asking, "What number multiplied by 3 equals 54?" Through recall or multiplication tables, we quickly find that 18 x 3 = 54.
-
Mental Math: With practice, many individuals can solve 54 ÷ 3 mentally by breaking down the numbers. For instance, you could think of 54 as 30 + 24, then divide each part by 3 (30 ÷ 3 = 10 and 24 ÷ 3 = 8), and finally add the results (10 + 8 = 18).
Real-World Applications of Division: Beyond the Classroom
The principles of division are applied extensively across various fields:
-
Cooking and Baking: Dividing ingredients proportionally for scaling recipes. If a recipe calls for 54 grams of flour divided into three equal parts, each part would be 18 grams.
-
Finance: Calculating equal monthly payments on a loan or splitting expenses amongst roommates. If three roommates share a monthly bill of $54, each owes $18.
-
Engineering: Calculating dimensions and proportions in construction, design, or manufacturing processes. Dividing a 54-meter length into three equal sections results in three 18-meter sections.
-
Data Analysis: Determining average values or proportions in data sets. If three tests have a combined score of 54, the average score per test is 18.
-
Everyday Life: Sharing items evenly, calculating fuel efficiency (miles per gallon), determining the price per unit of an item, and countless other scenarios.
Exploring the Concept of Remainders
While 54 divided by 3 results in a whole number (18), not all division problems yield such clean results. Some divisions leave a remainder. A remainder is the amount left over when a number cannot be perfectly divided by another number. Understanding remainders is crucial for understanding the limitations and possibilities of division.
For example, if we divide 55 by 3, we get 18 with a remainder of 1 (18 x 3 = 54, leaving 1). This remainder indicates that there's one unit left over after dividing 55 into three equal groups. Remainders are often represented as fractions or decimals, depending on the context.
Division and its Relationship to Other Mathematical Operations
Division is intrinsically linked to other arithmetic operations:
-
Multiplication: As previously mentioned, multiplication and division are inverse operations. They undo each other. If 3 x 18 = 54, then 54 ÷ 3 = 18.
-
Addition and Subtraction: Division can be conceptualized as repeated subtraction, while multiplication can be seen as repeated addition. These connections solidify the fundamental interconnectedness of arithmetic operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What if I want to divide a larger number by 3?
A: The same principles apply. You can use long division, repeated subtraction, or break down the number into smaller, more manageable parts to simplify the calculation.
-
Q: Are there any tricks or shortcuts to make division easier?
A: Yes! Familiarity with multiplication tables is extremely helpful. Also, practicing mental math strategies like breaking down numbers into easily divisible parts can significantly improve speed and accuracy.
-
Q: Why is division important in higher-level mathematics?
A: Division forms the basis of many more complex concepts such as fractions, decimals, algebra, calculus, and numerous other mathematical fields. A solid understanding of division is essential for advanced mathematical study.
-
Q: What if the divisor is zero?
A: Division by zero is undefined in mathematics. It's a concept that leads to inconsistencies and paradoxes within mathematical systems. Therefore, division by zero is not a permissible operation.
Conclusion: Beyond the Simple Answer
While the answer to 54 divided by 3 is simply 18, this article has demonstrated that this seemingly basic calculation holds much deeper meaning and relevance. Understanding the underlying principles of division, exploring different solution methods, and recognizing its wide-ranging applications are essential for building a solid mathematical foundation. By grasping these concepts, you'll not only improve your mathematical skills but also enhance your ability to tackle complex problems in various aspects of life. The seemingly simple act of dividing 54 by 3 opens a window into the fascinating and interconnected world of mathematics. It is a testament to the power of understanding fundamental concepts and applying them to solve real-world problems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
164 Lbs In Kilos
Sep 18, 2025
-
Calories 6 Nuggets Mcdo
Sep 18, 2025
-
18 24 As A Percentage
Sep 18, 2025
-
Three Subject Verb Disagreements
Sep 18, 2025
-
25 Mph To Km
Sep 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 54 Divided By 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.