2 X 3 9
renascent
Sep 17, 2025 · 6 min read
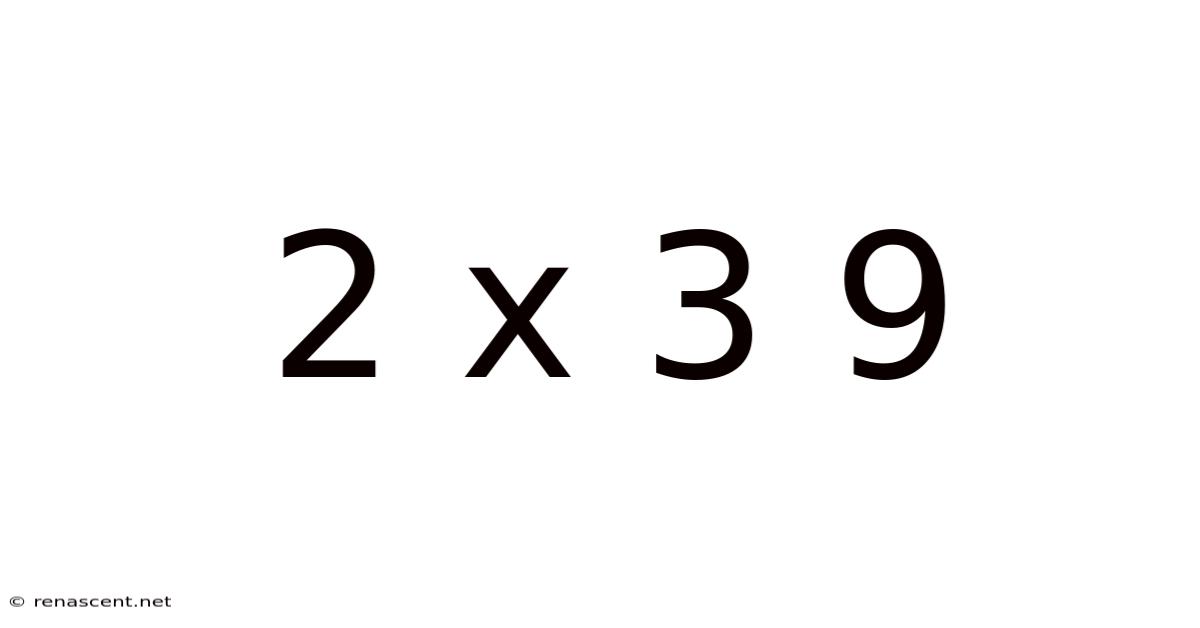
Table of Contents
Decoding 2 x 3 = 9: Exploring Mathematical Fallacies and Creative Problem Solving
The seemingly simple equation, 2 x 3 = 9, is inherently false within the standard framework of arithmetic. However, this incorrect statement opens a fascinating door to explore mathematical fallacies, creative problem-solving approaches, and the power of alternative perspectives. This article delves into the reasons why 2 x 3 cannot equal 9 in traditional mathematics, examines potential scenarios where such a result might appear valid (though always within a carefully constructed context), and finally, explores how this seemingly erroneous equation can spark creative thinking and inspire novel solutions to problems.
Introduction: The Illusion of Truth
The statement "2 x 3 = 9" is demonstrably false. Multiplication, a fundamental arithmetic operation, defines 2 x 3 as the sum of two 3s (3 + 3 = 6), or three 2s (2 + 2 + 2 = 6). The result is unequivocally 6, not 9. The assertion that 2 x 3 = 9 instantly flags a mathematical error. This error, however, provides a springboard for discussions about logical fallacies, mathematical manipulations, and the importance of understanding underlying assumptions.
Unveiling the Fallacy: Where the Error Lies
The fallacy behind claiming 2 x 3 = 9 often stems from a deliberate or accidental misapplication of mathematical rules or a manipulation of visual representations. Let's examine some common scenarios that might appear to support this incorrect equation:
-
Misleading Visuals: A cleverly designed diagram might be presented to visually "prove" 2 x 3 = 9. This often involves subtly altering the shapes or sizes of objects to create an illusion. The visual trickery disguises the true nature of the multiplication process.
-
Incorrect Grouping or Re-arrangement: A manipulation might involve incorrectly grouping or rearranging numbers to arrive at the desired, yet false, result. This could involve misinterpreting the order of operations or applying an operation inappropriately.
-
Introducing Extraneous Variables: The fallacy could be introduced by adding an extraneous variable without clearly stating its inclusion or its impact on the equation. This variable might subtly alter the calculation, creating a false impression.
-
Altered Number Systems: While unlikely in a straightforward context, the equation could hold true within a deliberately constructed or unconventional number system. This would require a redefinition of fundamental arithmetic operations and the properties of numbers themselves. We'll explore this possibility later.
Exploring Alternative Mathematical Frameworks: Where 2 x 3 Might Seemingly Equal 9
While 2 x 3 will always equal 6 within the standard decimal number system, we can explore scenarios where a similar outcome might appear, albeit with significant caveats:
-
Modular Arithmetic: In modular arithmetic, we work with remainders after division. For instance, in modulo 3 arithmetic (denoted as mod 3), we consider only the remainder when dividing by 3. In this system, 2 x 3 = 6, and the remainder when 6 is divided by 3 is 0. While not directly equal to 9, this illustrates how different number systems can produce different results.
-
Abstract Algebra: Within the realms of abstract algebra, particularly in groups and rings, it's possible to define operations that behave differently than standard multiplication. A carefully constructed algebraic structure could potentially yield a result analogous to 2 x 3 = 9, but this would involve a highly specialized and non-intuitive definition of "2," "3," "x," and "=".
-
Custom Number Systems: We can theoretically design a unique number system where the symbols "2" and "3" represent different values than their usual decimal counterparts, and the operation "x" represents a non-standard multiplication. By carefully defining these elements, we could make the equation 2 x 3 = 9 true within the constraints of this custom system. This is akin to creating a new mathematical language. However, it would have limited applicability outside its specific framework.
Problem Solving Inspired by the Fallacy: A Creative Approach
Rather than dismissing the equation "2 x 3 = 9" as simply wrong, let's explore its potential to stimulate creative thinking:
-
Identifying the Error: The most crucial lesson is in identifying and dissecting the error. This hones analytical and critical thinking skills. The process of finding where the fallacy lies is a valuable exercise.
-
Building a Narrative: The false equation can serve as a starting point for a creative writing prompt. A story could be constructed around a world where 2 x 3 = 9, exploring the consequences of such a different mathematical reality. This exercise engages imagination and narrative construction.
-
Designing a Puzzle: The equation can be incorporated into a mathematical puzzle or riddle. The challenge could involve identifying the hidden manipulation or devising a context where the equation holds true within a specific, limited system. This promotes problem-solving skills and logical reasoning.
-
Exploring Alternative Perspectives: The exploration of alternative mathematical frameworks, even if hypothetical, broadens our understanding of mathematical concepts and encourages out-of-the-box thinking.
-
Developing Critical Thinking: By actively questioning the equation and investigating its potential validity within different contexts, we develop critical thinking skills, essential for navigating complex problems in any field.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Can 2 x 3 ever equal 9 in standard mathematics? No, in standard arithmetic, 2 x 3 will always equal 6. Any claim that it equals 9 indicates a mathematical error or a manipulation of the symbols.
-
Are there any real-world applications where 2 x 3 = 9 might appear? No, there are no real-world applications within the context of standard mathematics where 2 x 3 would legitimately equate to 9. Any such application would rely on a deliberate misrepresentation or the use of a non-standard system.
-
Why is it important to understand mathematical fallacies? Understanding fallacies helps us develop critical thinking, identify misleading arguments, and build a stronger foundation in mathematics and logic. It prevents us from accepting false claims without proper scrutiny.
-
Can this equation be used as a teaching tool? Absolutely! The equation "2 x 3 = 9" can serve as an excellent teaching tool to highlight mathematical fallacies, promote critical thinking, and stimulate creative problem-solving within a controlled learning environment.
Conclusion: Beyond the Falsehood
The seemingly simple, yet incorrect, equation "2 x 3 = 9" provides a surprisingly rich opportunity for learning and creative exploration. While it is fundamentally false within the framework of standard arithmetic, examining this statement reveals the importance of understanding mathematical principles, identifying logical fallacies, and appreciating the power of alternative perspectives in problem-solving. The equation serves as a reminder that questioning assumptions and embracing creativity are crucial components of both mathematical and broader intellectual development. The false premise opens doors to richer mathematical understanding and creative endeavors, highlighting the value of questioning and exploring unconventional ideas. It underscores the importance of critical thinking and analytical skills in navigating the complexities of the world around us, where accurate information and sound reasoning are paramount.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Square Root Of 130
Sep 18, 2025
-
Activity On Node Diagram
Sep 18, 2025
-
26 2 Miles In K
Sep 18, 2025
-
Clock Showing 2 30
Sep 18, 2025
-
56 Grams To Oz
Sep 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 X 3 9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.