81 F In C
renascent
Sep 16, 2025 · 5 min read
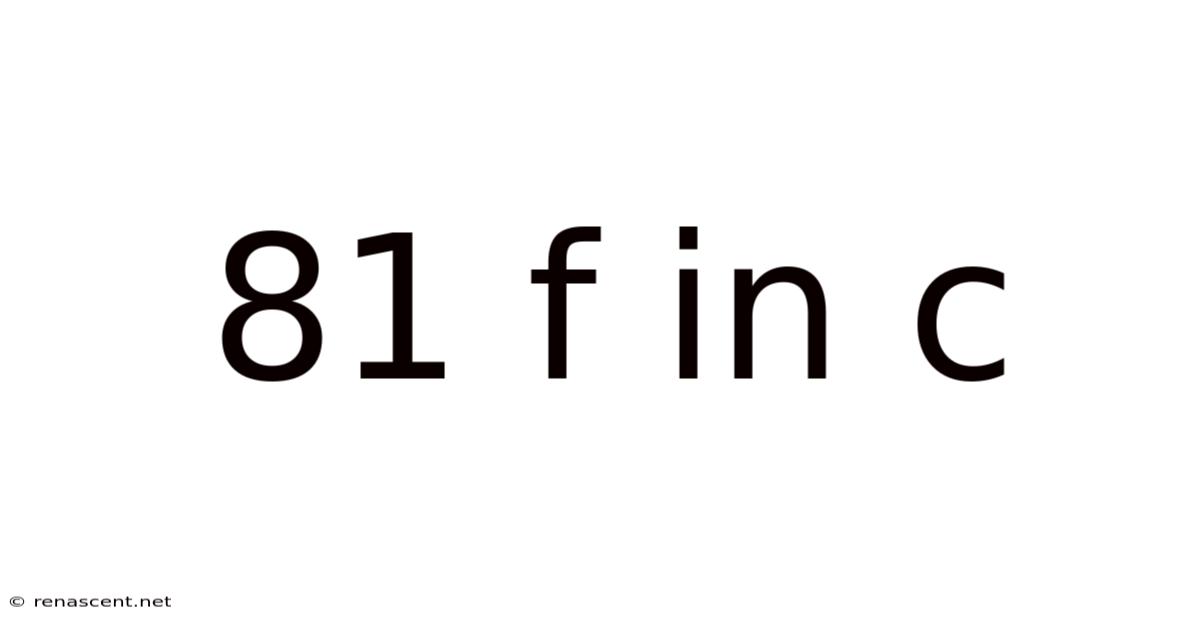
Table of Contents
Decoding 81°F in Celsius: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Conversions and Applications
Understanding temperature conversions is crucial in various fields, from everyday life to scientific research. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process of converting 81°F (Fahrenheit) to Celsius (°C), explaining the underlying principles, practical applications, and addressing frequently asked questions. We'll explore the historical context of these temperature scales, highlighting their differences and demonstrating the conversion calculation step-by-step. By the end, you'll not only know the Celsius equivalent of 81°F but also possess a solid understanding of temperature conversion and its significance.
Understanding Fahrenheit and Celsius
Before we jump into the conversion, let's establish a basic understanding of the two scales. Both Fahrenheit (°F) and Celsius (°C) are units used to measure temperature, but they differ significantly in their reference points.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): This scale was developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century. Its zero point was originally based on a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride, while the boiling point of water was set at 212°F. Today, the Fahrenheit scale is primarily used in the United States and a few other countries.
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius was developed by Anders Celsius in the 18th century. It uses the freezing point of water (0°C) and the boiling point of water (100°C) at standard atmospheric pressure as its reference points. The Celsius scale is the most widely used temperature scale globally and is the standard unit for scientific applications.
Converting 81°F to Celsius: The Formula and Calculation
The conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius involves a simple linear formula. To convert from Fahrenheit to Celsius, we use the following equation:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Let's apply this formula to convert 81°F:
-
Subtract 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature: 81°F - 32 = 49
-
Multiply the result by 5/9 (or 0.5556): 49 × 5/9 ≈ 27.22
Therefore, 81°F is approximately equal to 27.22°C.
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversions
The ability to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius is essential in many contexts:
-
Meteorology: Weather reports often provide temperatures in both Fahrenheit and Celsius. Understanding the conversion allows for easy interpretation regardless of the scale used.
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes may specify temperatures in either Fahrenheit or Celsius. Accurate conversion ensures consistent results.
-
Medicine: Body temperature is often measured in both scales. Knowing the conversion is critical for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
-
Engineering and Manufacturing: Many industrial processes require precise temperature control. Conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius is crucial for ensuring compatibility and accuracy across different systems.
-
Scientific Research: Scientific experiments often require precise temperature measurements and conversions are essential for data analysis and interpretation across international collaborations.
Beyond the Conversion: Understanding Temperature and its Effects
While converting 81°F to Celsius provides a numerical equivalent, it's equally important to understand the implications of this temperature. 27.22°C falls within a relatively comfortable range for humans, generally considered pleasant for most individuals. However, the perception of comfort can vary based on factors such as humidity, wind speed, and individual tolerance.
At this temperature, water remains liquid, and various biological processes function optimally. However, in agricultural applications, 27.22°C might indicate conditions that require irrigation or shade for certain crops to thrive. The effects of temperature depend heavily on the specific context.
A Deeper Dive into the History and Development of Temperature Scales
The Fahrenheit and Celsius scales weren't the only attempts at standardizing temperature measurement. Other scales, like Réaumur and Kelvin, have also been developed, each with its own unique reference points and applications.
The Kelvin scale, for example, is an absolute temperature scale, meaning it starts at absolute zero – the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases. This scale is widely used in scientific research, particularly in fields like thermodynamics and physics.
The historical development of these scales reflects the evolving understanding of heat, temperature, and their relationship to matter. Early attempts were often based on arbitrary reference points, reflecting the limited understanding of the fundamental principles governing thermal behavior. The development of more sophisticated scales, such as the Kelvin scale, demonstrates the advancements in scientific understanding and technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: Why are there different temperature scales?
A: Different temperature scales were developed independently at different times, based on different reference points and using varied methods of measurement. This resulted in a variety of scales, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The continued use of multiple scales reflects historical inertia and the differing needs and preferences of various sectors and countries.
- Q: Which temperature scale is more accurate?
A: All scientifically valid temperature scales are equally accurate within their defined ranges. The choice of scale depends on the application and context. Celsius is generally preferred in science for its logical and convenient reference points. Kelvin is crucial in thermodynamics because it relates to absolute zero. Fahrenheit persists mainly due to its historical use in specific regions.
- Q: Can I use a different formula to convert 81°F to Celsius?
A: While the formula provided is the most common and straightforward, other equivalent formulas could be derived. However, they would essentially perform the same calculation, just perhaps with a different arrangement of steps. Sticking to the standard formula ensures clarity and avoids potential errors.
- Q: What is the significance of 0°C and 100°C?
A: 0°C represents the freezing point of water, and 100°C represents the boiling point of water under standard atmospheric pressure. These points are fundamental reference points for the Celsius scale, defining its range and providing a convenient and widely understood benchmark.
- Q: Is there an online calculator to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius?
A: Yes, many online calculators are available that can perform this conversion instantly. However, understanding the formula allows for independent calculation and a more thorough grasp of the process.
Conclusion
Converting 81°F to Celsius, yielding approximately 27.22°C, is a simple yet fundamental process with far-reaching implications. This guide provides not only the calculation but also contextualizes it within the broader understanding of temperature scales, their history, and applications in diverse fields. Understanding temperature conversions is not just a matter of mathematical calculation; it's a gateway to appreciating the significance of temperature in our world and its impact on various aspects of life, from everyday comfort to scientific discovery. By mastering this seemingly simple conversion, you've taken a step towards a deeper comprehension of the physical world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
32 40 As A Percentage
Sep 16, 2025
-
Rules For Scientific Drawings
Sep 16, 2025
-
98 F In C
Sep 16, 2025
-
35 Kilometers To Miles
Sep 16, 2025
-
20 25 As A Percentage
Sep 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 81 F In C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.